Study Background
Non-communicable diseases (NCDs) are increasingly becoming a public health challenge, particularly in resource-limited settings, where there is limited access to preventive care, early detection, and health literacy. Nevertheless, there is an immense potential of digital technologies to contribute to the enhancement of overall community health. Similarly, the WHO PEN Disease Interventions for Primary Healthcare in Low-Resource Settings has demonstrated evidence of improving NCD outcomes. Nevertheless, its effectiveness in the Indian settings has not been explored.
Mixed methods, quasi-experimental across 4 states.
This study adopts a multi-site, quasi-experimental design with a mixed-method approach to evaluate the comparative effectiveness of a digital intervention platform and the WHO Package of Essential Non-communicable Disease Interventions (WHO PEN) against a control group receiving no intervention. The study is being implemented in the urban poor settings across four geographically and socio-culturally diverse sites in India. The study will span three years and execute three distinct phases to achieve the three stated objectives. The interventions will be deployed in the third phase of the study, and will include follow-up evaluations at 3 months, 6 months, 9 months and 12 months post-intervention.
Inclusion Criteria :
- Participants should be between the ages of 18-70.
- Individuals who have Smartphones.
- They should have Diabetes, CVD, or both.
Exclusion Criteria:
- Individuals below 18 and over 70 years.
- Individuals who do not have Diabetes or CVD.
- Not having Smartphones.
- Having a terminal illness and not being available for follow-up.
- Individuals with co-morbidities that would interfere with the intervention.
- Individuals with severe mental health conditions.
320 Participants for qualitative tools
To ensure that each site implements all three arms while preserving feasibility and minimizing contamination, the study will use a clustered quasi-experimental design at the local community level:
To meet objective 1, both the quantitative and qualitative data will be collected. At each site, eight focus group discussions (FGDs) will be conducted in community settings, with ten individuals participating in each group. The IDIs will be conducted among 10 individuals from the community and 10 community health workers. The Knowledge, Attitude, and Practice questionnaire, along with the other validated assessment tools, will be administered to 80 individuals from each site.
To meet objective 2, a total of 80 participants will be enrolled across four zones at each site to obtain their feedback on the developed digital platform.
To meet objective 3, participants at each site will be assigned to one of three study arms based on the site’s designated intervention:
- Digital Intervention Arm: Participants will receive access to a mobile and web-based digital health platform developed by FHTS, designed to promote NCD screening, health education, and behavior modification through interactive modules, personalized reminders, and self-tracking tools.
- WHO PEN Arm: Participants will receive structured screening, counselling, and management services as per the WHO PEN protocols 1 & 2, implemented through trained healthcare providers and community health workers.
- Control Arm: Participants will receive only routine health services available in their local setting,
- without any structured digital or WHO PEN-based intervention.
Urban slums:
Qualitative Tools:
In-Depth Interviews (IDIs).
In-depth Interviews (IDIs) will be conducted with participants from community settings and community health workers to explore their experiences, perceptions, and the barriers or facilitators related to the digital interventions and the WHO PEN program.

Focus Group Discussions (FGDs).
Focus Group Discussions (FGDs) will be conducted with community members and community health workers at each site to understand their collective perspectives on NCD prevention and digital engagement.

Quantitative Data Collection Tools:
Data Analysis
Interviews and focus groups will be audio-recorded, transcribed verbatim, and translated to English where necessary. A thematic analysis approach will be applied using NVivo software. Triangulation across all the data sources will enhance validity. Data will be analyzed using SPSS (Version 29) and R. Heuristic evaluation will involve the estimation of severity ratings, frequency of usability issues, time taken to complete tasks, and inter-rater reliability. Descriptive statistics will include means (SDs), medians (IQRs), and proportions to summarise baseline characteristics. Between interventions and control arms, the analysis would be carried out by ANCOVA or generalised linear models, adjusting for baseline values, cluster effects, and site-level covariates. Statistical significance will be set at p < 0.05, with confidence intervals at 95%.
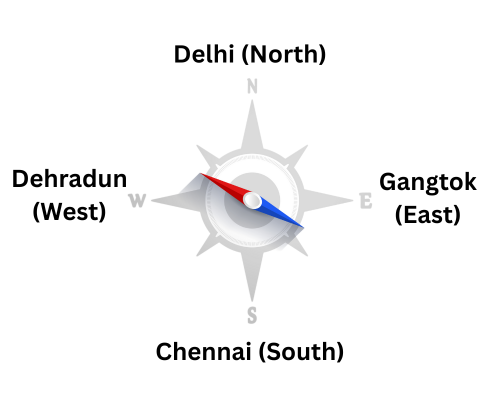
Ethical approval has already been obtained from the Institutional Human Ethics Committees (IECs) of all participating sites from Delhi, Dehradun, Sikkim and Chennai.
- Delhi: Foundations of Healthcare Technologies Society (FHTS) obtained its ethical approval in December 2024 with IRB approval No. FHTS/IHEC/2024/01.
- Dehradun: Government Doon Medical College (GDMC) obtained its ethical approval in June 2025, with approval number GDMC/IEC/2025/12.
- Sikkim: Sikkim University obtained its ethical approval in June 2025, with IRB approval number SU/REG/F-1/03/2019/Vol-II/771.
- Chennai: Panimalar Medical College Hospital & Research Institute obtained its ethical approval in February 2025, with approval number, PMCHRI-IHEC-286.